Text boxes and decorations
SPDS, uni.kn
2023 01 01
Source:vignettes/text_decorations.Rmd
text_decorations.RmdThis vignette explains the unikn functions for plotting graphical elements and text decorations. (See the vignette on colors for general information on colors, color palettes, and corresponding functions, or the more specialized vignettes on color recipes and institutional colors.)
Please install and/or load the unikn package to get started:
Overview
Beyond providing support for colors, unikn provides functions for plotting graphical elements (like boxes) and text decorations (with colored backgrounds or underlining). Before illustrating these functions, please note some caveats:
Plotting text (i.e., graphically rendering characters) is rarely a good idea. In contrast to the vector fonts used by DTP programs, plotted text typically does not scale (when changing the size of images) and cannot be recognized automatically (e.g., copied, indexed, or scraped). Hence, the following functions should only be used when no better solutions are available (e.g., for adding text to graphs, or for obstructing automatic text recognition).
Like all other templates, our renderings are subject to constraints and limitations. For instance, as any standard installation of R lacks the prescribed “Theinhardt” fonts, we only mimic the official design specifications (in Arial, sans serif).
That said, digital decorations can be useful to emphasize or structure information, provided that they can be produced easily and flexibly. The unikn package helps preventing common mistakes by novices (e.g., boxes or lines extending beyond text, or step-functions in multi-line headings) and can be customized and improved by expert users. Hence, we hope that the following functions are useful for plotting graphical elements (e.g., boxes, logos, etc.) and help you achieve a uniform look when styling presentations or visualizations.
Please load the unikn package to get started:
Plotting empty slides and boxes
As the text functions of unikn add styled text to an existing plot, we must first create a plot to which we can add text. unikn provides 2 basic functions for creating new plots:
-
slideplots an empty canvass (a rectangular box or frame); -
xboxplots a colored box with an X in its top right corner.
Here are both commands with their default settings:
slide() # plot default slide
xbox() # plot default xbox
Both functions accept additional arguments to customize their appearance.
Colors
The background and border colors of slides can be changed by setting
their col, border, and lwd
arguments:
slide(col = pal_seeblau[[1]], border = Petrol, lwd = 5) # set colors of slide background and border
slide(col = pal_peach[[2]], border = NA) # colored slide without a border
Similarly, the background color of xboxes can be changed by the
col argument:
xbox(col = Pinky) # set background color of xbox
Dimensions
By default, both slide and xbox fill the
entire plotting region (i.e., all margins are set to 0).
The width of a slide is set to 4/3 of its height (of 1). To change
this default, use the dim argument for specifying the
slide’s x- and y-dimensions, respectively:

Note that changes in slide dimensions are invisible when viewing images interactively, as R automatically scales images to the size of the canvass. They mostly affect the relation between metrics when adding elements to an object.
Similarly, an xbox has the default dimensions of a unit square (i.e.,
dim = c(1, 1)). To change this default, use the
dim argument for specifying the xbox’s x- and
y-dimensions, respectively:
The two strokes of the X (in the top right corner) are orthogonal
when viewing the xbox at the aspect ratio indicated by
dim (i.e., here: at a ratio of width x = 1 to height y =
2). When viewing the box at any different aspect ratio, the X appears to
be distorted. Hence, viewing and printing plots at the desired aspect
ratio helps when creating an xbox.
Plotting styled text
There are three main functions for plotting text with decorations:
-
mark()allows highlighting text with colored background boxes; -
uline()allows underlining text with colored lines; -
post()allows posting text in rectangularxboxelements.
In addition, there are 2 auxiliary functions:
-
headline()allows plotting headlines with colored background boxes; -
url_unikn()allows formatting URLs the uni.kn way.
The following sections illustrate the functions and their main options in turn.
Mark text
The mark() function allows highlighting text by plotting
it with colored background boxes (to provide the functionality of
“Markieren”):
By default, mark() assumes that we want to add
highlighted text to an existing plot. The text labels to be added are
provided (as a character vector) by the labels argument,
their coordinates as the corresponding x and y
arguments. Various text decorations (i.e., text and background colors,
text sizes, and font types) can be set by specifying additional
arguments (i.e., col, col_bg,
cex, and font, respectively):
# Some pre-existing plot:
n <- 20
set.seed(1)
par(mar = c(0, 0, 0, 0))
plot(x = runif(n), y = runif(n), type = "p", pch = 16, cex = 20, col = grey(0, .2),
axes = FALSE, xlab = "", ylab = "")
# Add 1 marked label:
mark(labels = "Some messy plot", x = .02, y = .9)
# Add 2 more marked labels:
mark(labels = c("Note something here.", "More highlighting here."),
x = c(.1, .6), y = c(.2, .4),
col_bg = c(pal_seeblau[[2]], pal_peach[[3]]), cex = 1.2)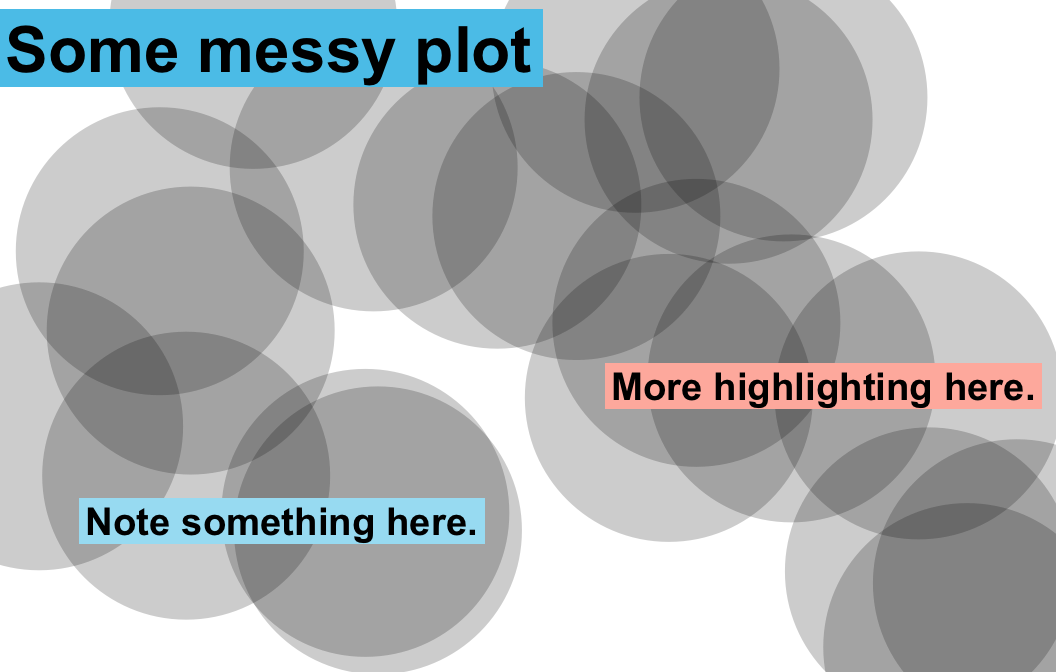
If no pre-existing plot is available, setting the
new_plot argument to either "blank"
or "slide" will generate a new default plot (by calling the
slide() function described above):
# A sentence to plot:
s <- c("Markieren",
"ist ein Bestandteil",
"von Studieren.")
# Create a new plot (of type "slide"):
mark(labels = s,
x = 0, y = .85, y_layout = .03,
col_bg = Seeblau,
cex = 1.5,
new_plot = "slide")
# Add text to the same plot:
mark(labels = s,
x = 0, y = .40, y_layout = .03,
col_bg = pal_pinky[[2]],
cex = 1.5,
new_plot = "none")
Rather than providing explicit x and
y coordinates for all text elements in labels,
the calls above defined an initial coordinate and used a numeric
y_layout argument to fix the distance between consecutive
text labels (to a value of .03).
As an alternative to numeric coordinates and position values,
x_layout and y_layout also accept some special
values (as character strings):
-
x_layoutaccepts:-
x_layout = "center"for centering labels horizontally (on the first label or the middle),
-
x_layout = "left"left-justifies labels (on the first label or the middle), and
-
x_layout = "right"right-justifies labels (on the first label or the middle).
-
-
y_layoutaccepts:-
y_layout = "even"for an even distribution of labels across the available y-space, and
-
y_layout = "flush"to omit space between adjacent labels (as iny_layout = 0).
-
Thus, the position and orientation of the text labels can be
controlled by using the x_layout and y_layout
options:
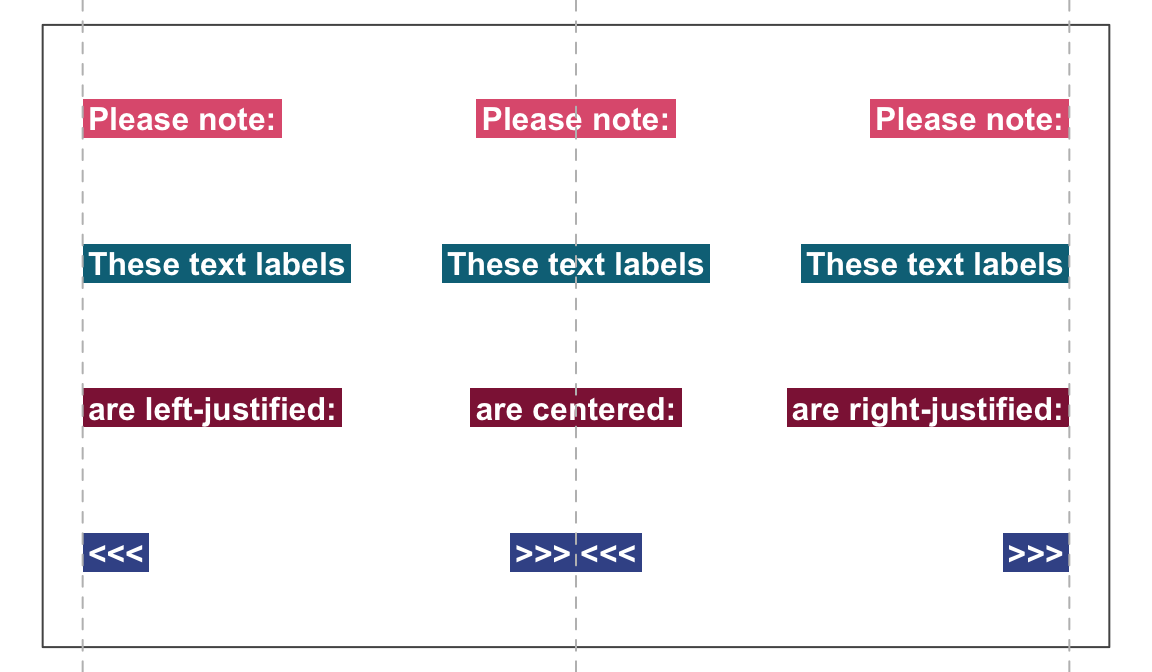
See ?mark for details.
Underline text
The uline() function allows emphasizing text by plotting
it with colored underlining (to provide the functionality of
“Unterstreichen”):
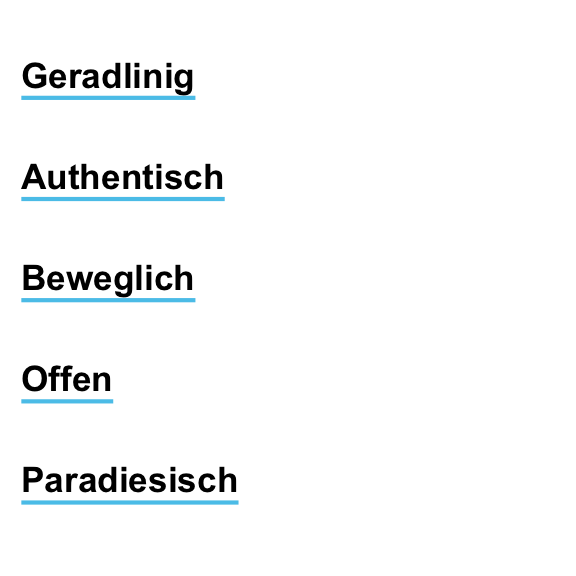
As with mark() above, the uline() command
distinguishes between creating a new plot (by setting
new_plot to either "blank" or
“slide”) or adding to a pre-existing plot (by using the
default new_plot = "none"):
lbl_uline <- c("This is neat, true, and terribly important")
uline(labels = lbl_uline, new_plot = "blank", y = .6, cex = 1.1) # create a new plot
uline(labels = "(which is why we underline it).", y = .45, cex = 1) # add to plot
The arguments for text elements (labels), text positions
(x, y, y_layout), and text
properties and decorations (col, col_bg,
cex, and font) work as they do for
mark(). For instance, shorter vectors are recycled to match
the length of labels:
slogan <- c("Geradlinig", "Farbenfroh", "Beweglich", "Bunt", "Paradiesisch")
uline(labels = slogan,
x = c(0, .5), y = .9, y_layout = "even",
col = c("black", Bordeaux), col_bg = c(Seeblau, Seegruen),
cex = 1.1, font = 2, new_plot = "blank")
The position and orientation of the text labels can be controlled by
using the x_layout and y_layout options:
Post text
The post() function allows adding text to a
rectangular xbox (to provide the functionality of
“Merken”):

By default, post() assumes a pre-existing
xbox to which the text elements of labels are
to be added.
For square boxes, setting new_plot to "xbox"
creates a new xbox with its default dimensions of
dim = c(1, 1).
By adjusting its color and text arguments, post() allows
creating simple badges or logos:
# Badge (to view as 250 x 250 pixel):
post(labels = "ToDo", y = .35,
col = "white", col_bg = pal_signal[[1]],
cex = 3, font = 2, new_plot = "xbox")
# Badge (to view as 250 x 250 pixel):
post(labels = "R", y = .35,
col = "white", col_bg = pal_seeblau[[5]],
cex = 8, font = 2, new_plot = "xbox")

Another potential use of post() is for creating images
providing contact details:
address <- c("Dr. B. F. Skinner", " ",
"Department of Psychology",
"Office Z101",
"Tel.: +49 7531 88-0815",
"Fax: +49 7531 88-0810",
"b.f.skin@uni-konstanz.de")
post(labels = "Contact",
y = .7,
cex = 1.2, font = 2,
col_bg = Petrol,
new_plot = "xbox") # create new plot
post(labels = address,
y = .5, y_layout = .03,
new_plot = "none") # add to plot
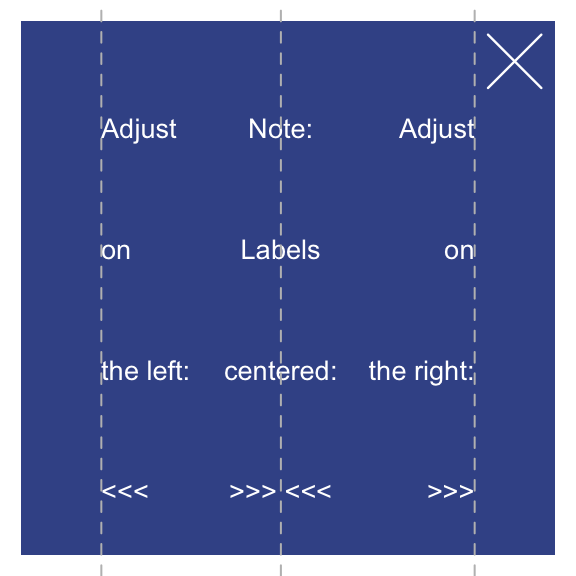
As above, the position and orientation of the text labels can be
controlled by using the x_layout and y_layout
options:
Headings
The heading() function makes it easy to create
recognizable headings:

By default, the function creates a new slide (i.e.,
new_plot = "slide") and positions the text elements
of labels on its left edge (i.e., x = 0,
y = .8 and y_layout = "flush"). When headings
violate the official recommendations, a message is provided:

Re-arranging words helps to avoid step-wise titles (see p. 25 of the CD manual):
# Beware of step-wise arrangements:
heading(labels = c("Ich", "bin keine", "gute Headline."))
#> Step-wise titles are discouraged: Consider re-arranging?

When colors are left unspecified, heading() selects
colors that are appropriate for the number of elements in
labels (i.e., shades of Seeblau for
col_bg = "default"). However, default colors can be
overwritten by setting the col and col_bg
arguments:
heading(labels = c("Ene,", "mene, miste,", "es rappelt", "in der Kiste."),
col = "white", col_bg = c(Pinky, Seegruen, Bordeaux, Karpfenblau))
URLs
One of the more obscure rules (on p. 31 of the CD manual) concerns
the rendering of URLs, in which typical web patterns (like “http” or
“www”) are to be omitted and replaced by a typographical dash (which is
longer than a hyphen). The url_unikn utility function
allows formatting URLs the uni.kn way:
my_url <- url_unikn("https://www.uni-konstanz.de/") # input URL
my_url # formatted URL
#> [1] "– uni-konstanz.de"
# Put URL at bottom of an xbox:
post(labels = my_url, x = .05, y = .1, font = 4,
col_bg = pal_seeblau[[5]], new_plot = "xbox")
Resources
The following versions of unikn and corresponding resources are currently available:
| Type: | Version: | URL: |
|---|---|---|
| A. unikn (R package): | Release version | https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=unikn |
| Development version | https://github.com/hneth/unikn/ | |
| B. Online documentation: | Release version | https://hneth.github.io/unikn/ |
| Development version | https://hneth.github.io/unikn/dev/ |
Vignettes
The following vignettes provide instructions and examples for using the unikn colors, color palettes, and functions:
| Nr. | Vignette | Content |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Colors | Colors and color functions |
| 2. | Color recipes | Recipes for color-related tasks |
| 3. | Institutional colors | Creating color palettes for other institutions |
| 4. | Text | Text boxes and decorations |
